This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. Read our cookie policy
Aspirating Smoke Detection
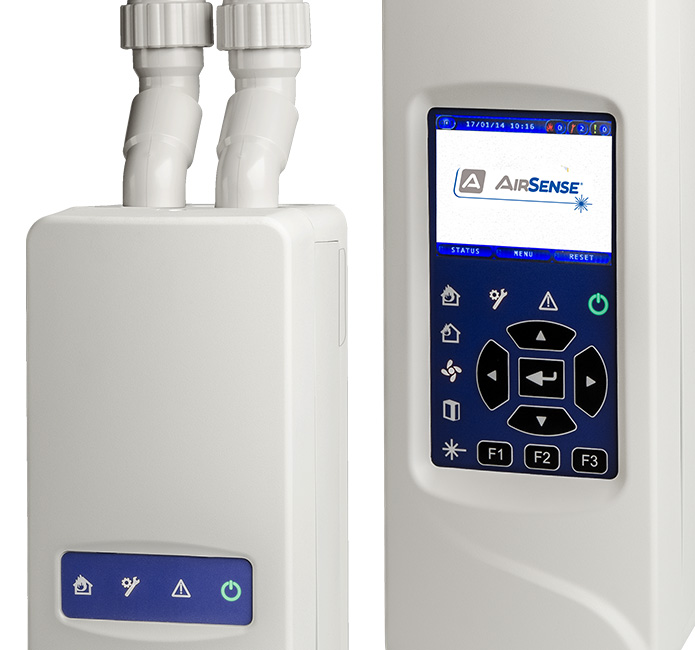
Aspirating smoke detectors (ASD) are a type of fire detection device that uses a small fan to pull in air from a protected area and pass it through a detection chamber. The air is then analysed for the presence of smoke particles. The system can be configured to sample air from specific locations or from a general area. These detectors are highly sensitive and are able to detect smoke at an early stage of fire, making them particularly useful for detecting smoldering fires.
ASD typically consist of three main components: a sample pipe network, a sample point and a detector unit. The sample pipe network is a network of pipes that are used to transport air from the protected area to the detector unit. The sample point is the location where air is drawn into the pipe network. The detector unit is where the air is analysed for smoke particles.
ASDs can be connected to a building's fire alarm system, and can also be integrated with other building systems such as HVAC systems and sprinkler systems. They are typically used in large buildings such as airports, museums and other public buildings where early detection and rapid response is critical.
However, these detectors can be affected by environmental factors such as dust, dirt and insects. They also require regular maintenance, cleaning and calibration to ensure proper operation.
Aspirating smoke detectors (ASDs) are highly sensitive smoke detectors that use a fan to draw air samples from a protected area through a network of pipes to a central detection unit. Aspirating smoke detectors can detect smoke before it is visible to the naked eye meaning they are ideal for environments such as data centres and large storage facilities where early warning of fire is essential.
From £1,244.58 Inc VAT